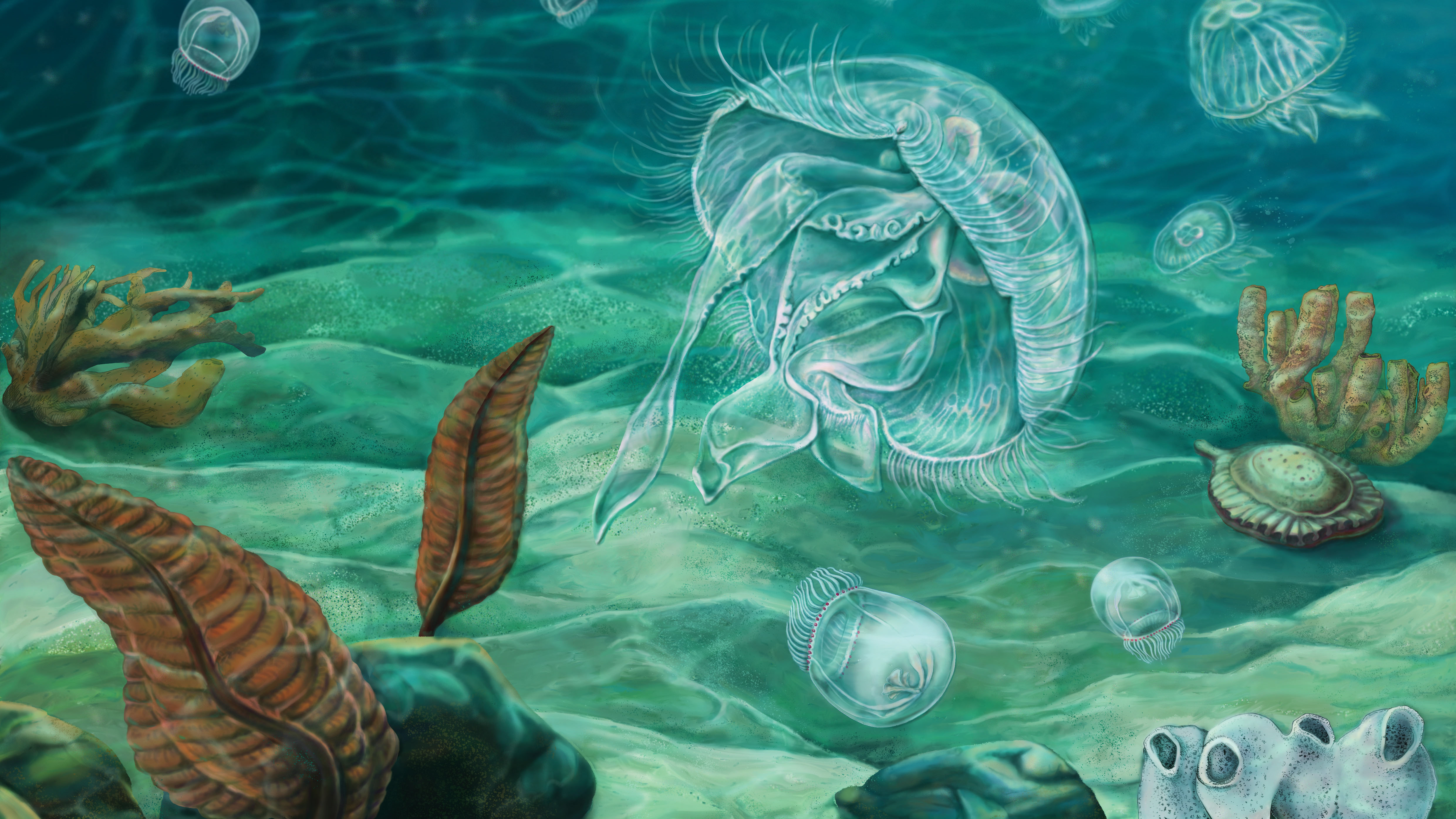
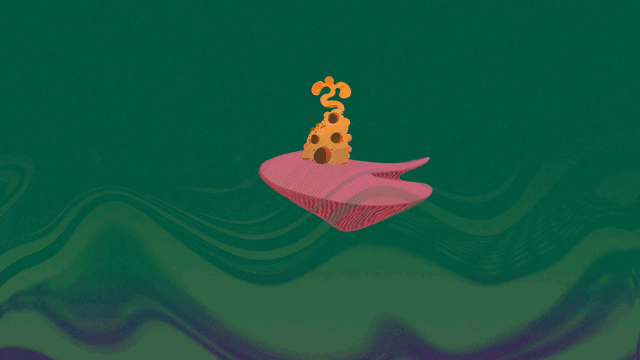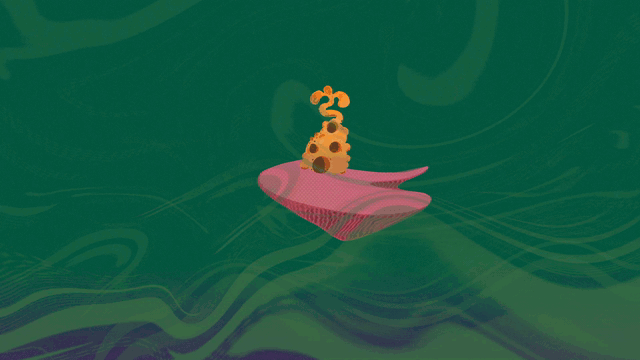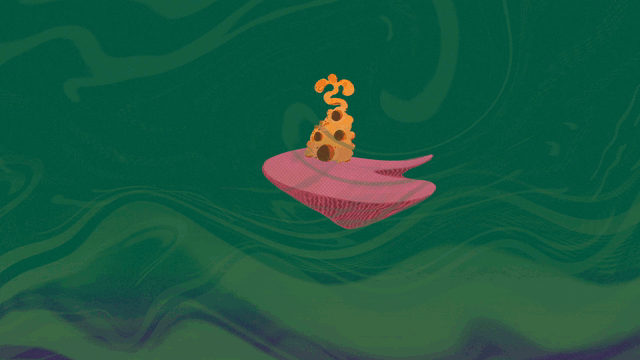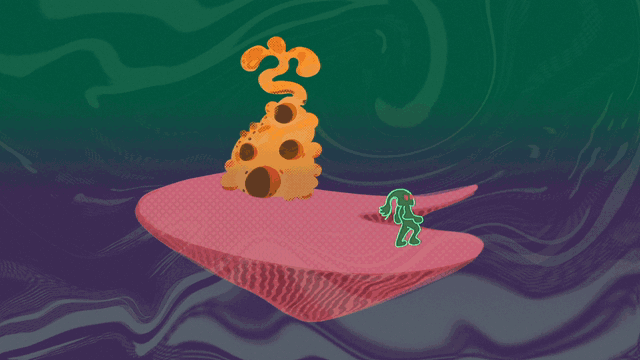
Cover Image for the Journal of Neuroscience, volume 45, Issue 20
This 3D model of the hydrozoan jellyfish (Polyorchis penicillatus) features its motor nerve net in yellow. The nerve net consists of electrically coupled motor neurons arranged in two rings connected via four radial branches. At right are four snapshots of jellyfish swimming motion with fluid wakes included. Fabian Pallasdies and colleagues developed a biophysical model of the motor nerve net, linking its activity to a biomechanical fluid simulation in order to understand how the jellyfish achieves stable and efficient swimming motion. See the article by Pallasdies et al: